Timeline Arranger#
The timeline arranger is the main area where the song is composed. It consists of a collection of events, such as regions, positioned against time. Some events (such as regions) will open separate windows for further editing when clicked.
The timeline arranger is split into a top arranger that remains fixed on top and a bottom arranger below it. This way you can pin tracks you want to always be visible at the top.
Arranger Objects#
The following arranger objects can exist inside the timeline.
Regions#
Regions (or clips) are containers for events or data (such as MIDI notes and audio clips - see below) that can be edited in an editor. Regions can be repeated, like below.

区域#
The following types of regions exist.
音频区域#
Audio regions contain audio clips from audio files.

音频区域#
Audio regions belong to track lanes and appear inside Audio tracks.
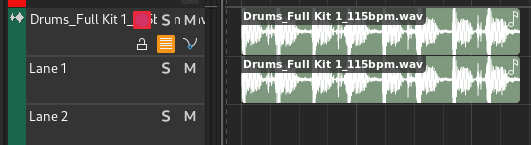
Audio track with audio region#
Double-clicking an audio region will bring up the Audio Editor.
MIDI 区域#
MIDI regions contain MIDI notes.

MIDI 区域#
MIDI regions belong to track lanes and appear inside MIDI or Instrument tracks.
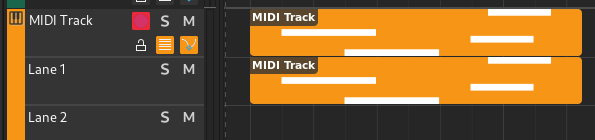
MIDI track with MIDI region#
Double-clicking a MIDI region will bring up the Piano Roll.
Automation Regions#
Automation regions contain automation events.
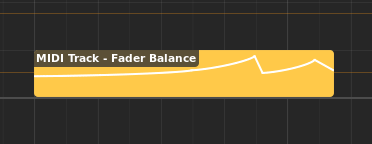
自动化区域#
Automation regions appear inside automation lanes.
Automation lane with automation region#
Double-clicking an automation region will bring up the Automation Editor.
Chord regions#
Chord regions contain sequences of chords.

和弦区域#
Chord regions appear inside the chord track.

Chord track with chord region#
Double-clicking a chord region will bring up the Chord Editor.
标记#
Markers are used to mark the start of a logical section inside the song, such as Chorus or Intro.

標記#
Markers appear inside the marker track.

Marker track with marker#
There are two special markers that signify the start and end of the song that are used for exporting the song and cannot be deleted.
音阶#
Scales are used to indicate the start of a section using a specific musical scale.

Scale#
Scales appear inside the Chord track.

Chord track with scale#
Editing Regions#
The following operations apply to regions.
循环#
Regions can be repeated, and hence they have editable loop points and a clip start position in the Editor ruler to modify the looping (repeating) behavior.
Regions can also be looped inside the timeline, by moving the cursor to the bottom-left or bottom-right edge of the region, then clicking and dragging.
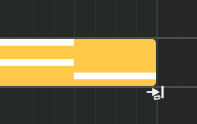
Looping (loop-resizing) a region#
備註
If the region is already repeated, it cannot be resized anymore until its loop points match exactly the region’s start and end points.
Link-Moving#
Linked regions can be created by holding down Alt while moving.
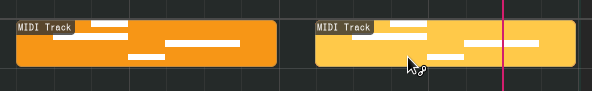
Link-moving a MIDI region#
You can verify that a link exists on a region by the link icon that shows in the top right.

Linked MIDI regions#
Renaming#
Regions can be renamed by selecting them and pressing F2.
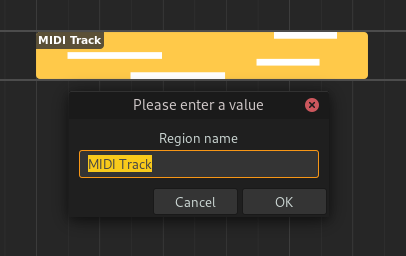
Renaming a region#
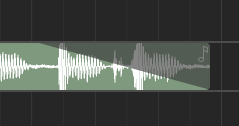
Adjusting Fades#
Audio regions can have fades. Fades are gradual increases or decreases in the level of the audio signal, and their positions can be adjusted by clicking and dragging the top left/right corners of the region.

Adjusting fade out point (click & drag)#

Adjusting fade out point (drop)#
Clicking and dragging the grey part up or down will adjust the curviness of the fade.

Adjusting curviness#
The type of fade algorithm used can also be changed by right-clicking on the fade and selecting .
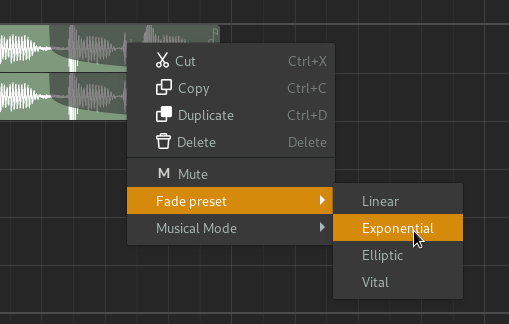
Fade context menu#
The various types of fade algorithms available are illustrated below.
備註
All audio regions have some additional, built-in fade in and fade out that cannot be disabled. This is used to avoid clipping and should be unnoticable.